The Art and Science of ATM Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Art and Science of ATM Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of ATM Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of ATM Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide

The ubiquitous Automated Teller Machine (ATM) has become an integral part of modern financial landscapes. From bustling city centers to remote villages, these machines provide convenient and secure access to banking services, enabling individuals to withdraw cash, check balances, and perform various financial transactions. But what goes into the creation of these indispensable devices? This article delves into the intricate world of ATM manufacturing, exploring the design, technology, and processes that bring these machines to life.
Understanding the ATM Ecosystem
ATM manufacturing is a multifaceted process involving a complex interplay of diverse components, technologies, and expertise. The journey from concept to deployment encompasses various stages:
- Design and Engineering: This phase involves conceptualizing the ATM’s physical design, considering factors like user interface, security features, and operational requirements. Engineers work diligently to ensure the machine is robust, user-friendly, and compliant with industry standards.
- Component Sourcing: ATM manufacturers rely on a vast network of suppliers for critical components, including cash dispensers, card readers, touchscreens, and security systems. Each component must meet rigorous quality standards to ensure seamless operation and reliability.
- Assembly and Testing: The manufacturing process involves assembling the various components into a functional unit. Rigorous testing is conducted at each stage to verify performance, security, and adherence to regulatory standards.
- Software Development: ATM software is crucial for managing transactions, communicating with banks, and ensuring secure operations. Software developers create and integrate complex algorithms to handle financial transactions, user authentication, and data encryption.
- Deployment and Maintenance: Once manufactured, ATMs are deployed at various locations, often in collaboration with financial institutions. Regular maintenance and software updates are essential to ensure optimal performance and security.
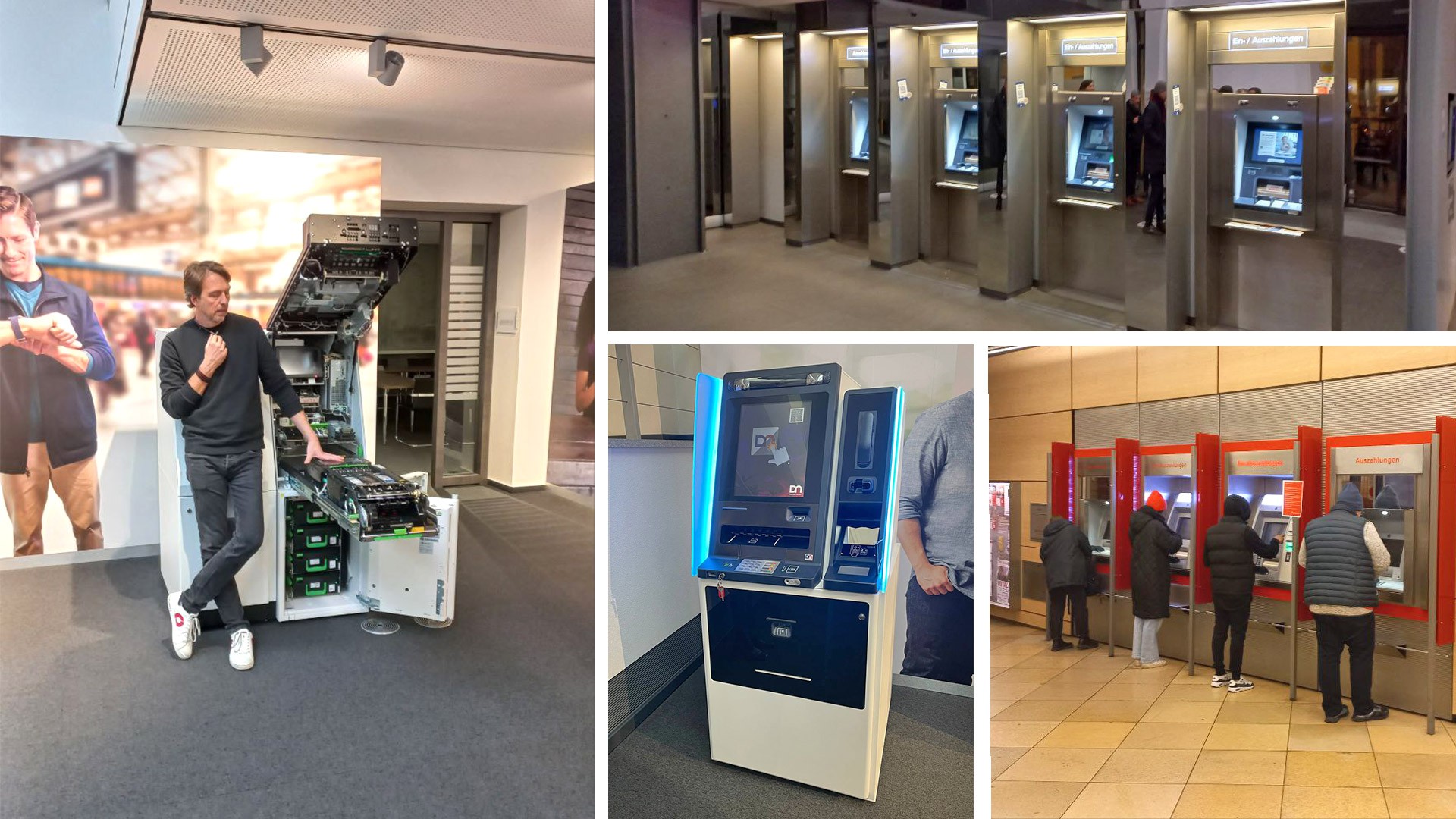
Key Components of an ATM
ATM functionality relies on a carefully integrated combination of hardware and software components:
- Cash Dispenser: This component, often referred to as a "cash cassette," securely stores and dispenses cash in various denominations. Modern ATMs utilize advanced dispensing mechanisms for reliable and accurate cash delivery.
- Card Reader: This component reads magnetic stripe cards or chip-based cards, verifying the user’s identity and authorizing transactions. Secure card reading technology plays a vital role in preventing fraud and unauthorized access.
- Touchscreen: The touchscreen provides the user interface for navigating menus, selecting transactions, and entering PINs. User-friendly design and intuitive navigation are crucial for an enjoyable user experience.
- Security System: ATMs are equipped with sophisticated security systems to protect against unauthorized access, theft, and vandalism. These systems may include physical barriers, surveillance cameras, and tamper-proof mechanisms.
- Network Connectivity: Modern ATMs are connected to bank networks via secure communication protocols, enabling real-time transaction processing and data exchange.
The Role of Technology in ATM Manufacturing
Technological advancements have revolutionized ATM manufacturing, leading to enhanced functionality, improved security, and greater user convenience. Key technological trends influencing ATM design and development include:
- Biometric Authentication: ATMs are increasingly incorporating biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, to enhance security and streamline user authentication.
- Mobile Integration: Many modern ATMs allow users to initiate transactions via mobile apps, enabling remote access and seamless integration with digital banking services.
- Data Analytics: Advanced data analytics capabilities enable ATM manufacturers to monitor machine performance, identify potential issues, and optimize operational efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered systems are being integrated into ATMs to enhance fraud detection, personalize user experiences, and optimize cash management.
The Importance of ATM Manufacturing
ATM manufacturing plays a pivotal role in modern economies by:
- Expanding Financial Inclusion: ATMs provide access to financial services in geographically diverse locations, enabling individuals and businesses to manage their finances conveniently.
- Driving Economic Growth: By facilitating secure and efficient financial transactions, ATMs contribute to economic growth and development.
- Supporting Business Operations: ATMs are essential for businesses, enabling them to manage cash flow, pay employees, and conduct transactions efficiently.
- Enhancing Security: ATM manufacturing prioritizes security features, ensuring safe and reliable access to financial services.
FAQs on ATM Manufacturing
Q: What are the typical costs associated with manufacturing an ATM?
A: ATM manufacturing costs vary widely depending on the model, features, and technological advancements incorporated. Generally, basic models start from around $5,000, while advanced models with sophisticated features can cost upwards of $20,000 or more.
Q: What are the key regulatory standards governing ATM manufacturing?
A: ATM manufacturers must comply with various regulatory standards, including those related to security, data privacy, and accessibility. These standards are typically set by national and international governing bodies.
Q: What are the future trends in ATM manufacturing?
A: The future of ATM manufacturing is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, biometric authentication, and mobile integration. These technologies will enable more personalized experiences, enhanced security, and greater convenience for users.
Tips for ATM Manufacturers
- Focus on User Experience: Design ATMs with intuitive interfaces and ergonomic features to ensure a positive user experience.
- Prioritize Security: Implement robust security measures to protect against fraud, theft, and unauthorized access.
- Embrace Technological Advancements: Stay abreast of technological trends and incorporate innovative features to enhance functionality and competitiveness.
- Foster Collaboration: Collaborate with financial institutions, software developers, and other stakeholders to optimize ATM design and deployment.
Conclusion
ATM manufacturing is a complex and dynamic industry that plays a vital role in facilitating financial transactions and enhancing the accessibility of financial services. By continuously innovating and adapting to evolving technological landscapes, ATM manufacturers are ensuring the ongoing relevance and reliability of these indispensable machines. As technology continues to advance, ATMs are poised to become even more integrated into our daily lives, offering greater convenience, security, and personalized experiences.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of ATM Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!