The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Balance
Related Articles: The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Balance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Balance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Balance
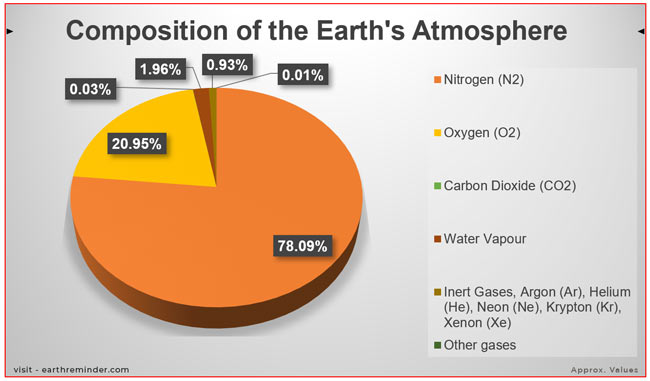
The Earth’s atmosphere, a thin, gaseous layer enveloping our planet, plays a crucial role in sustaining life. It acts as a protective shield, regulating temperature, filtering harmful radiation, and facilitating weather patterns. Understanding the composition of this vital layer, specifically the proportions of its constituent gases, is paramount to comprehending its multifaceted functions and the delicate balance that governs our planet’s climate.
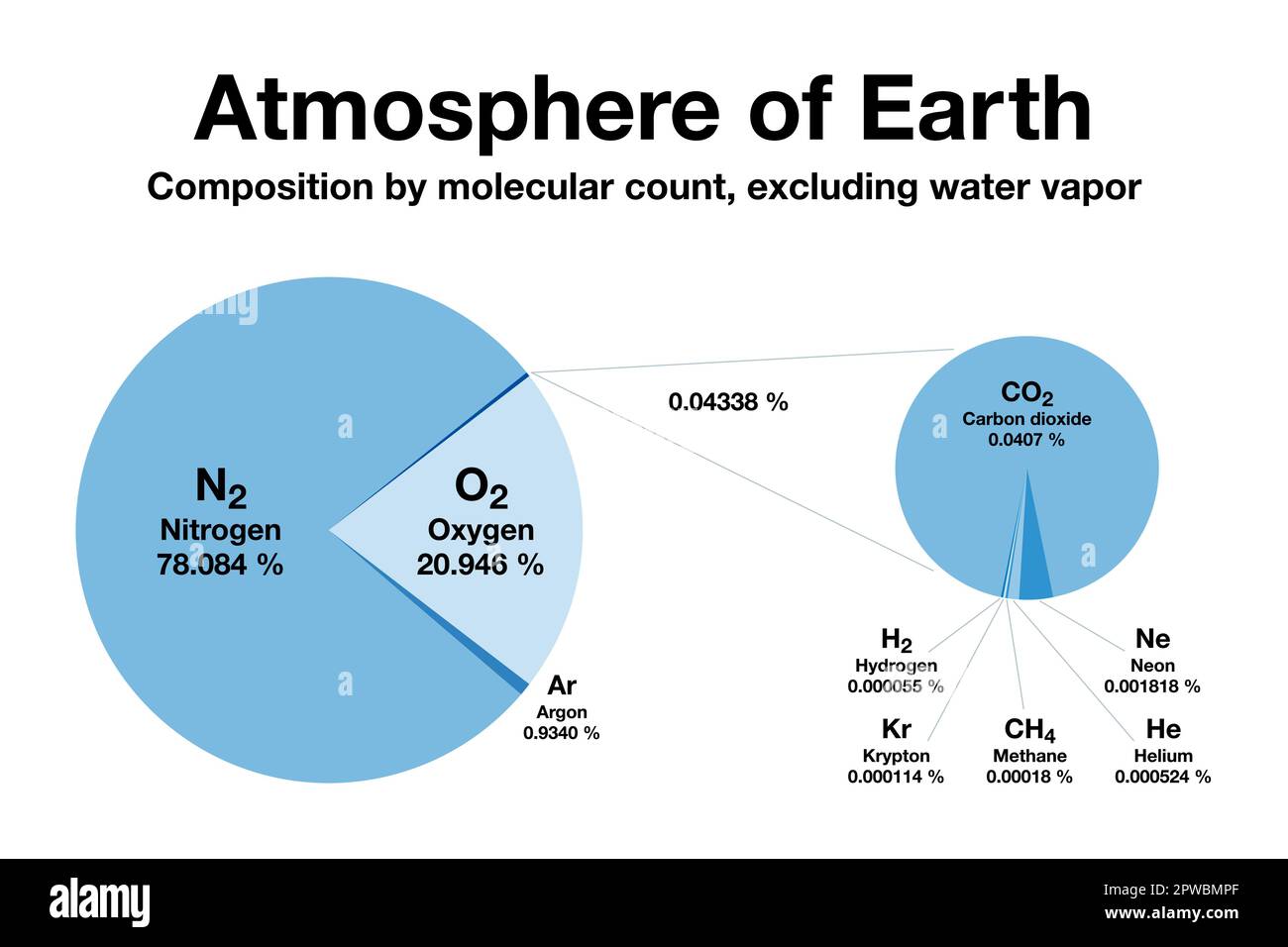
The Major Players: Nitrogen and Oxygen
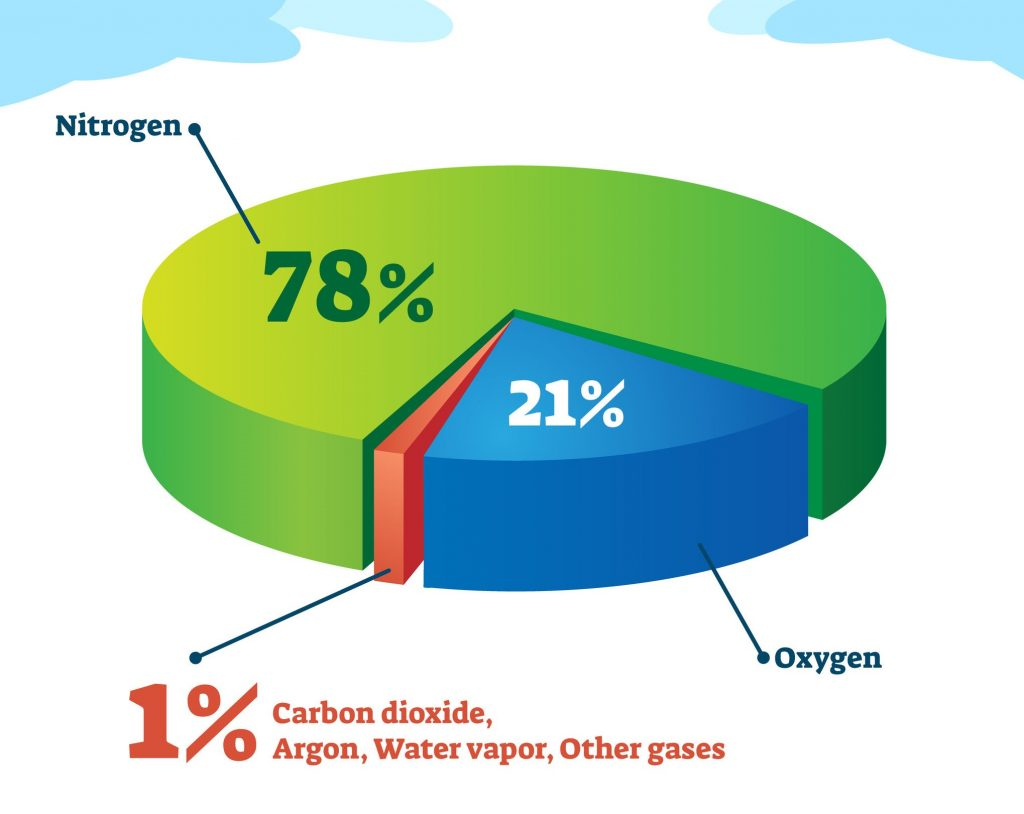
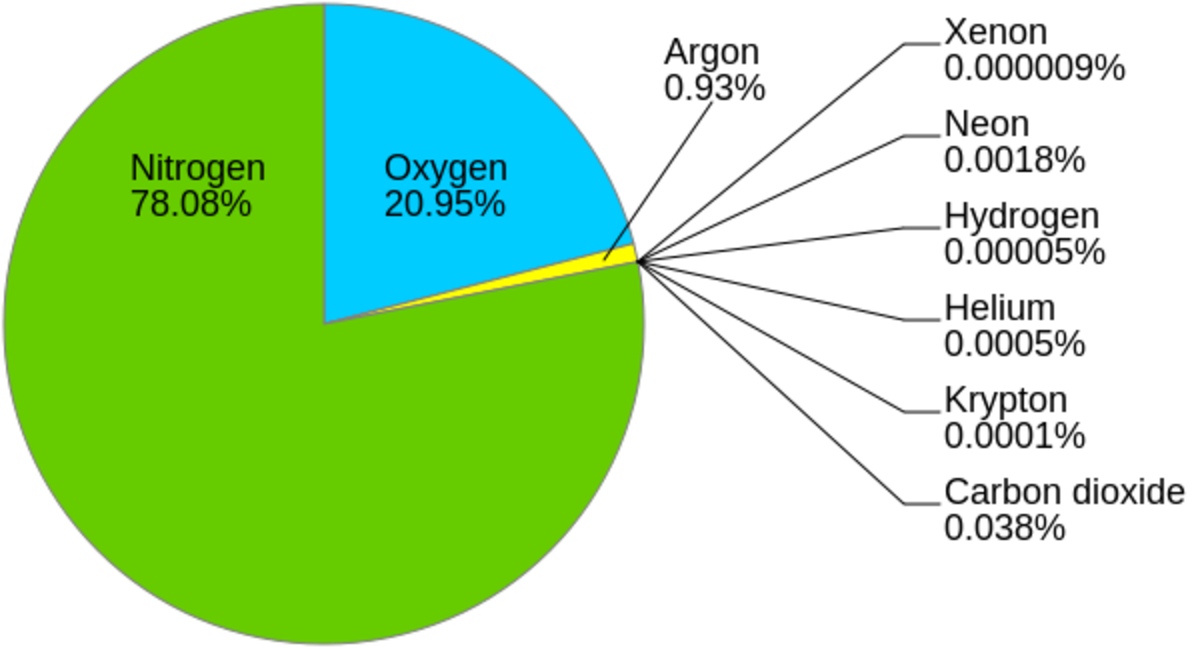
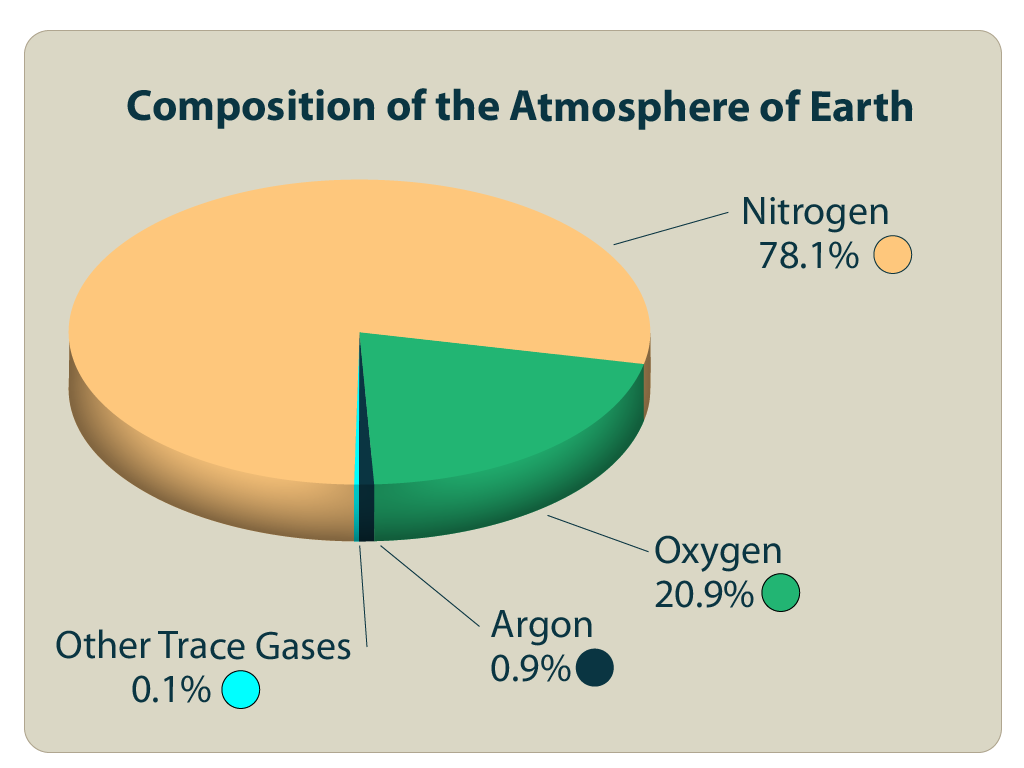
The Earth’s atmosphere is predominantly composed of two gases: nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2). These gases constitute approximately 99% of the atmosphere’s volume. Nitrogen, at a staggering 78%, serves as an inert gas, playing a relatively passive role in atmospheric processes. Oxygen, at 21%, is the essential gas for respiration, enabling life to thrive.
The Minor Components: A Crucial Role
While nitrogen and oxygen dominate the atmosphere, the remaining 1% comprises a diverse array of gases, each playing a critical role in various atmospheric processes. These include:
- Argon (Ar): This inert gas makes up about 0.93% of the atmosphere and is primarily a byproduct of radioactive decay.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): While present in a relatively small proportion (around 0.04%), carbon dioxide plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s temperature through the greenhouse effect.
- Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH4), Krypton (Kr), Hydrogen (H2), Ozone (O3), and Xenon (Xe): These gases, though present in trace amounts, contribute significantly to atmospheric processes such as the ozone layer’s formation, temperature regulation, and chemical reactions.
The Dynamic Nature of Atmospheric Composition
The composition of the atmosphere is not static but rather dynamic, constantly evolving due to various natural and anthropogenic influences. Volcanic eruptions, for instance, release significant amounts of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and other gases, while human activities like burning fossil fuels contribute to increased carbon dioxide levels.
Understanding the Importance of Atmospheric Composition
The proportions of gases in the atmosphere are crucial for maintaining a habitable environment. Understanding the composition and its variations is critical for:
- Climate Change Studies: Monitoring the changes in atmospheric composition, particularly greenhouse gas concentrations, is essential for understanding and mitigating climate change.
- Air Quality Management: The composition of the atmosphere directly influences air quality, impacting human health and the environment.
- Weather Forecasting: Atmospheric composition plays a significant role in weather patterns, influencing temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- Space Exploration: Understanding the composition of Earth’s atmosphere is essential for designing spacecraft and developing strategies for space exploration.
The Greenhouse Effect: A Balancing Act
The greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon where certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere, is vital for maintaining Earth’s temperature within a habitable range. While essential for life, the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations due to human activities has led to global warming, posing a significant threat to the planet’s ecosystem.
The Ozone Layer: A Protective Shield
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, absorbs most of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, shielding life on Earth from its damaging effects. However, human-induced depletion of the ozone layer due to the release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) has raised concerns about increased UV radiation levels, leading to health risks.
The Role of Atmospheric Composition in Weather Patterns
Atmospheric composition significantly influences weather patterns. For instance, water vapor, a variable component of the atmosphere, plays a crucial role in cloud formation and precipitation. Variations in atmospheric composition can lead to changes in temperature, wind patterns, and precipitation, impacting weather events across the globe.
FAQs on Atmospheric Composition
1. What is the primary source of nitrogen in the atmosphere?
The primary source of nitrogen in the atmosphere is volcanic eruptions, which release significant amounts of nitrogen gas.
2. How does the composition of the atmosphere affect climate?
The composition of the atmosphere, particularly the concentration of greenhouse gases, directly influences the Earth’s temperature and climate.
3. What are the major sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Major sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere include natural processes like respiration and volcanic eruptions, and human activities like burning fossil fuels.
4. How is the ozone layer being depleted?
The ozone layer is being depleted by human-made chemicals, primarily chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which react with ozone molecules and break them down.
5. What are the consequences of climate change?
Climate change has various consequences, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, changes in precipitation patterns, and shifts in ecosystems.
Tips for Reducing Atmospheric Pollution
- Reduce energy consumption: Use energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, and consider alternative sources of energy like solar and wind power.
- Conserve water: Reduce water usage by taking shorter showers, fixing leaks, and watering lawns efficiently.
- Support sustainable transportation: Choose public transportation, cycling, or walking instead of driving alone.
- Reduce waste: Recycle and compost to minimize landfill waste.
- Support environmental policies: Advocate for policies that promote clean energy and sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The composition of Earth’s atmosphere is a vital component of our planet’s complex system. Understanding the proportions of gases and their dynamic interactions is crucial for comprehending the intricate processes that govern climate, weather, and life itself. By recognizing the impact of human activities on atmospheric composition, we can strive to protect this precious resource and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Balance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!